Camallanoidea
| Camallanoidea | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
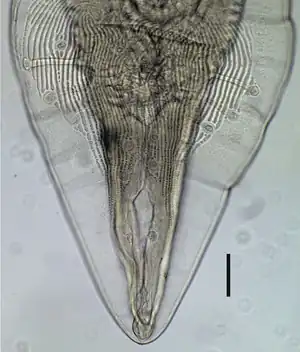
Vorderende von Physaloptera ngoci | ||||||||||||
| Systematik | ||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||
| Wissenschaftlicher Name | ||||||||||||
| Camallanoidea | ||||||||||||
| Railliet & Henry, 1915 |
Die Camallanoidea sind eine Überfamilie der Rollschwänze mit etwa 700 Arten.[1] Sie sind Parasiten des Magen-Darm-Trakts bei Wirbeltieren. Als Zwischenwirt dienen Ruderfußkrebse und Insekten.[2]
Merkmale
Der Schwanz ist lang und spitz und trägt gewöhnlich Phasmiden mit breiten Höhlen und auffälligen Poren. Die Ösophagusdrüsen sind uninukleär. Die Mundhöhle ist gut entwickelt und die inneren Lippenpapillen sind sehr klein. Die Larven haben keine Kopfhaken.[2]
Systematik
Hodda (2022) gliedert die Überfamilie in fünf Familien, vier Unterfamilien und 31 Gattungen:[1]
- Camallanidae Railliet & Henry, 1915
- Camallaninae Railliet & Henry, 1915
- Camallanides Baylis & Daubney, 1922
- Camallanus Railliet & Henry, 1915
- Malayocamallanus Jothy & Fernando, 1971
- Neoparacamallanus Bilqees & Akram, 1982
- Oncophora Diesing, 1851
- Paracamallanus Yorke & Maplestone, 1926
- Platocamallanus Bilqees & Akram, 1982
- Procamallanus Baylis, 1923
- Serpinema Yeh, 1960
- Camallaninae Railliet & Henry, 1915
- Physalopteridae Railliet, 1893 (Leiper, 1908)
- Physalopterinae Railliet, 1893
- Abbreviata Travassos, 1920
- Didelphyoptera Schulz, 1927
- Didelphysoma Schulz, 1927
- Kreisiella Jones, 1985
- Mooleptus Ozdikmen, 2010
- Mirzaloptera Wason & Johnson, 1977
- Neoleptus Specian, Ubelaker & Dailey, 1975
- Ochetocephalus Linstow, 1907
- Paraphysaloptera Gupta & Jehan, 1971
- Pentadentoptera Schachnasarova, 1949
- Physaloptera Rudolphi, 1819
- Polydelphyoptera Schulz, 1927
- Pseudabbreviata Lichtenfels & Quigley, 1968
- Pseudophysaloptera Baylis, 1934
- Skrjabinoptera Schulz, 1927
- Turgida Schulz, 1927
- Proleptinae Schulz, 1927
- Heliconema Travassos, 1919
- Paraleptus H.W. Wu, 1927
- Proleptus Dujardin, 1845
- Rasheedia Moravec & Justine, 2018
- Thubunaeinae Sobolev, 1949 (Chabaud, 1975)
- Physalopteroides Wu & Liu, 1940
- Thubunaea Seurat, 1914
- Physalopterinae Railliet, 1893
Einzelnachweise
- ↑ a b Mike Hodda: Phylum Nematoda: a classification, catalogue and index of valid genera, with a census of valid species. In: Zootaxa. 2022, Band 5114, Nummer 1, S. 118, doi:10.11646/zootaxa.5114.1.1.
- ↑ a b Alain G. Chabaud: Keys to subclasses, orders and superfamilies. Nr. 1 von Roy C. Anderson, Alain G. Chabaud, Sheila Willmott (Hrsg.): CIH keys to the nematode parasites of vertebrates. CABI, 1974, S. 12–13.