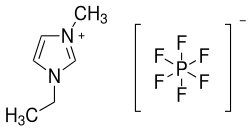
1-Ethyl-3-methylimidazoliumhexafluorophosphat
| Strukturformel | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||
| Allgemeines | |||||||||||||||||||
| Name | 1-Ethyl-3-methylimidazoliumhexafluorophosphat | ||||||||||||||||||
| Andere Namen |
| ||||||||||||||||||
| Summenformel | C6H11F6N2P | ||||||||||||||||||
| Externe Identifikatoren/Datenbanken | |||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||
| Eigenschaften | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molare Masse | 256,13 g·mol−1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Aggregatzustand |
fest | ||||||||||||||||||
| Schmelzpunkt | |||||||||||||||||||
| Sicherheitshinweise | |||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||
| Wenn nicht anders vermerkt, gelten die angegebenen Daten bei Standardbedingungen (0 °C, 1000 hPa). | |||||||||||||||||||
1-Ethyl-3-methylimidazoliumhexafluorophosphat ist eine ionische Flüssigkeit (auch: ionic liquid oder Flüssigsalz), also ein Salz, dessen Schmelzpunkt unter 100 °C liegt.
Eigenschaften
Mit einem Schmelzpunkt bei 58–62 °C handelt es sich bei 1-Ethyl-3-methylimidazoliumhexafluorophosphat um eine ionische Flüssigkeit. Als polare, hydrophobe Flüssigkeit wird es, wie viele ionische Flüssigkeiten, als Lösungsmittel in der Synthese eingesetzt.
Darstellung
1-Ethyl-3-methylimidazoliumhexafluorophosphat kann durch eine Anionenmetathese ausgehend von 1-Ethyl-3-methylimidazoliumchlorid und einem Hexafluorophosphat-Salz gewonnen werden.
Verwendung
1-Ethyl-3-methylimidazoliumhexafluorophosphat kann in Dual-Carbon-Akkumulatoren eingesetzt werden, wo es zu einer optimalen Energie-/Leistungsdichte beiträgt.[2] Thermodynamische Untersuchungen zeigen, dass eine Mischung aus Wasser und einem hohen 1-Ethyl-3-methylimidazoliumhexafluorophosphat eine hohe Leistungszahl von 0,9 in Absorptionskältemaschinen aufweist.[3]
Einzelnachweise
- ↑ a b c Datenblatt 1-Ethyl-3-methyl-imidazolium-hexafluorophosphat bei Sigma-Aldrich, abgerufen am 26. November 2021 (PDF).
- ↑ Xiaoyuan Shi, Wei Zhang, Jiafu Wang, Weitao Zheng, Keke Huang, Hengbin Zhang, Shouhua Feng, Hong Chen: (EMIm)+(PF6)− Ionic Liquid Unlocks Optimum Energy/Power Density for Architecture of Nanocarbon-Based Dual-Ion Battery. In: Advanced Energy Materials. Band 6, Nr. 24, 2016, S. 1601378, doi:10.1002/aenm.201601378.
- ↑ Yoon Jo Kim, Sarah Kim, Yogendra K. Joshi, Andrei G. Fedorov, Paul A. Kohl: Thermodynamic analysis of an absorption refrigeration system with ionic-liquid/refrigerant mixture as a working fluid. In: Energy. Band 44, Nr. 1, 2012, S. 1005–1016, doi:10.1016/j.energy.2012.04.048.
