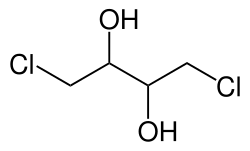
1,4-Dichlor-2,3-butandiol
| Strukturformel | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||
| vereinfachte Strukturformel ohne Angabe der Stereochemie | |||||||||||||||||||
| Allgemeines | |||||||||||||||||||
| Name | 1,4-Dichlor-2,3-butandiol | ||||||||||||||||||
| Andere Namen |
| ||||||||||||||||||
| Summenformel | C4H8Cl2O2 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Kurzbeschreibung |
weißer Feststoff[1] | ||||||||||||||||||
| Externe Identifikatoren/Datenbanken | |||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||
| Eigenschaften | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molare Masse | 159,01 g·mol−1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Aggregatzustand |
fest[1] | ||||||||||||||||||
| Schmelzpunkt | |||||||||||||||||||
| Siedepunkt | |||||||||||||||||||
| Löslichkeit | |||||||||||||||||||
| Sicherheitshinweise | |||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||
| Wenn nicht anders vermerkt, gelten die angegebenen Daten bei Standardbedingungen (0 °C, 1000 hPa). | |||||||||||||||||||
1,4-Dichlor-2,3-butandiol ist eine chemische Verbindung aus der Gruppe der Diole und Chlorhydrine.
Gewinnung und Darstellung
1,4-Dichlor-2,3-butandiol kann durch Reaktion von trans-1,4-Dichlor-2-buten mit tert-Butanol oder Kaliumpermanganat gewonnen werden.[6][7] Ebenfalls möglich ist die Darstellung durch Chlorhydrinierung von Butadien.[8]
Die meso-Form kann durch Reaktion von 1-Chlorbut-3-en-2-ol[9] mit hypochloriger Säure erhalten werden.[10]
Eigenschaften
1,4-Dichlor-2,3-butandiol ist ein weißes kristallines Pulver,[1] das sehr gut löslich in Ethanol ist.[5]
Einzelnachweise
- ↑ a b c d e f g Eintrag zu 1,4-Dichlor-2,3-butandiol, >98.0% bei TCI Europe, abgerufen am 22. Oktober 2023.
- ↑ Externe Identifikatoren von bzw. Datenbank-Links zu (2R,3R)-1,4-Dichlor-2,3-butandiol: CAS-Nr.: 221467-90-9, PubChem: 7516255, ChemSpider: 5834462, Wikidata: Q123165302.
- ↑ Externe Identifikatoren von bzw. Datenbank-Links zu 1,4-Dichlorobutane-2S-3S-diol: CAS-Nr.: 139165-54-1, PubChem: 7015309, Wikidata: Q82239554.
- ↑ a b Eintrag zu meso-1,4-Dichlor-2,3-butanediol, >98.0% bei TCI Europe, abgerufen am 22. Oktober 2023.
- ↑ a b CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics. CRC Press, ISBN 978-1-4987-5429-3, S. 160 (eingeschränkte Vorschau in der Google-Buchsuche).
- ↑ Koen P. M. Vanhessche, Zhi-Min Wang, K. Barry Sharpless: Asymmetric dihydroxylation of primary allylic halides and a concise synthesis of (−)-diepoxybutane. In: Tetrahedron Letters. Band 35, Nr. 21, 1994, S. 3469–3472, doi:10.1016/S0040-4039(00)73212-6.
- ↑ L. N. Owen: 59. The dichlorobutanediols. Part II. In: Journal of the Chemical Society (Resumed). Nr. 0, 1949, S. 241–243, doi:10.1039/JR9490000241.
- ↑ Milka Stojanowa-Antoszczyszyn, Jerzy Myszkowski, Antoni Z. Zielinski, Danuta Krawczyk: ChemInform Abstract: STUDIES ON THE SELECTIVE DIRECTING OF THE BUTADIENE CHLOROHYDROXYLATION REACTION TOWARDS DICHLOROBUTANEDIOL SYNTHESIS. In: Chemischer Informationsdienst. Band 7, Nr. 29, 1976, S. no–no, doi:10.1002/chin.197629151.
- ↑ Externe Identifikatoren von bzw. Datenbank-Links zu 1-Chlorbut-3-en-2-ol: CAS-Nr.: 671-56-7, PubChem: 12642, ChemSpider: 12121, Wikidata: Q123165164.
- ↑ R. M. Evans, L. N. Owen: 58. The dichlorobutanediols. Part I. The addition of hypochlorous acid to some chlorobutenols. In: Journal of the Chemical Society (Resumed). Nr. 0, 1949, S. 239–241, doi:10.1039/JR9490000239.